For Toyota Camry owners, encountering the 2004 Toyota Camry P2238 error code is not an uncommon occurrence, just like the P0770 error code in the Toyota Corolla 2003, especially if you use your car regularly. If you’ve experienced this issue, it indicates a problem with your car’s engine that requires attention. While there’s no need to panic, it’s essential to address the matter promptly.
Facing engine trouble can be concerning, but it’s essential to approach the situation calmly. To resolve the P2238 error code, it’s recommended to take your car to a certified mechanic or a reputable service center. Professional technicians will be able to diagnose the specific issue and implement the necessary repairs to get your car back in working order.
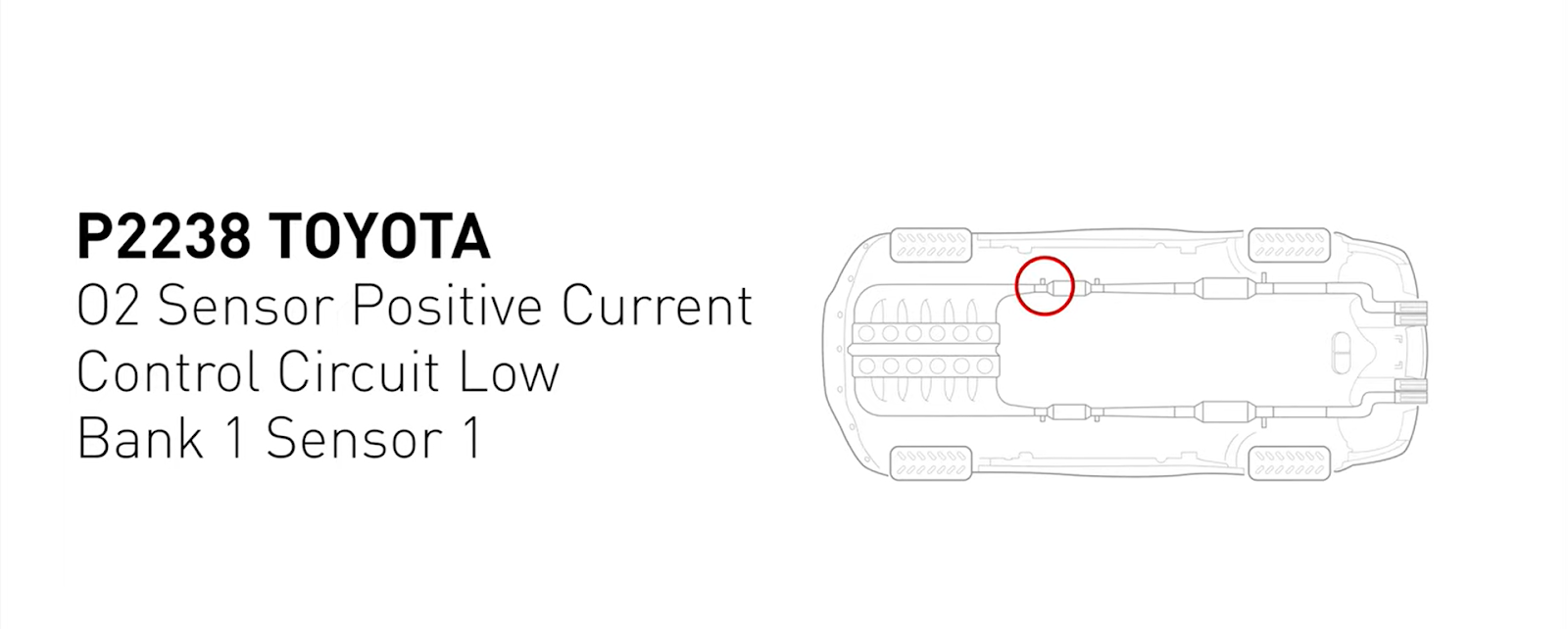
Understanding Code P2238 on a 2004 Toyota Camry
Code P2238 in a Toyota Camry from the year 2004 refers to a diagnostic trouble code related to the O2 Sensors Positive Current Control Circuit Low for Bank 1 Sensor 1. This code points to an issue with the circuitry responsible for controlling the engine’s voltage.
Since 1996, all cars have been equipped with an engine control module designated by the code P2238. When this code appears, it indicates that there is a problem with the engine control module’s operation due to various potential reasons. To accurately diagnose the cause in your specific situation, it’s crucial to have a qualified mechanic investigate the issue.
The engine control module (ECM) acts as the brain of your car, overseeing the air-fuel ratio and ensuring the safe functioning of the vehicle. If the ECM detects voltage levels outside the normal range, it may require the replacement of the O2 sensor to rectify the problem.
Taking prompt action and seeking professional assistance will help resolve the P2238 code and maintain the optimal performance of your 2004 Toyota Camry. Trusting in skilled mechanics and addressing the underlying cause will ensure your car operates smoothly and safely on the road.
Common Causes of Code P2238 in a 2004 Toyota Camry
Bad Oxygen Sensor:
The oxygen sensor, or O2 sensor, plays a crucial role in measuring the oxygen content of your exhaust emissions, helping determine engine efficiency. These sensors typically need replacement after covering 30,000 to 100,000 miles. It’s essential to address this promptly as a malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to concerning symptoms and affect the car’s performance.
Burnt, Broken, or Disconnected Wiring:
Corrosion in the O2 sensor’s wiring connectors or the presence of short circuits can be a possible explanation for code P2238. An issue with the heater circuit is often the culprit behind an O2 sensor problem. The internal failure of the O2 sensor’s heater circuit is the most common reason for encountering this code. Additionally, if the sensor’s cover is broken or removed, water may enter the backside, causing a short circuit, damaging the relay, or blowing the O2 sensor’s heater circuit fuse. Therefore, it is crucial to inspect the O2 sensor’s wires carefully.
Faulty PCM (Powertrain Control Module):
The Powertrain Control Module is responsible for managing various components and sensors in the engine. Its primary function is to collect data from different engine components and sensors to ensure smooth operation. While the PCM is designed to last the lifetime of your car, there is still a possibility of it becoming problematic over time. Although this occurrence is relatively rare in newer vehicle models, a malfunctioning PCM can trigger code P2238. If you notice indicators such as the check engine light illuminated, decreased engine power, or shifting problems, the PCM could be the potential cause.
Fixing Code P2238 on a 2004 Toyota Camry
- Check The Wire: Start by inspecting the wiring associated with the O2 sensor. Locate the wiring, which is positioned behind the cylinder head on the passenger side, where it connects to the harness for the driver’s side. Unplug the O2 sensor and use a multimeter set to the resistance or continuity setting to probe the sensor wires. Insert one cable end into a cable on the O2 sensor plug and touch the other end to either the positive or negative battery cable. If the multimeter beeps or shows no resistance, it indicates a wire has shorted. Access the harness and fix the short;
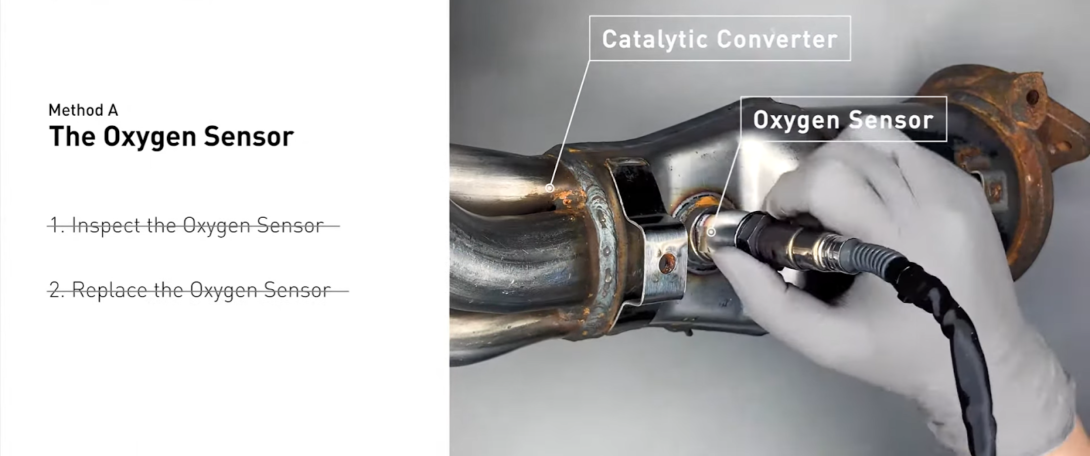
- Replace O2 Sensor: When the O2 sensor is broken or malfunctioning, it is essential to replace it. Although a bad sensor won’t prevent your vehicle from running, it’s advisable to replace it as soon as possible. To begin, use an OBD scanner to identify the problematic sensor. Let the engine cool down if it has been running recently and park your car on a level surface. Disconnect the sensor from the electrical connection and use a torque wrench and an oxygen sensor socket to unscrew it. Install the replacement sensor and secure it with a screw;
- Replace The ECM: The ECM (Engine Control Module) communicates with all the vehicle’s sensors and handles signal transmission. If the ECM malfunctions while the car is running, it can lead to code P2238. If necessary, consider replacing it. Locate the rectangular, silver module inside the engine chamber or elsewhere. After removing it due to a faulty ECM, use a socket wrench to reinstall the screws. Reconnect the battery, plug the electrical cables back into the ECM, and turn the key to start the car. In some cars with theft deterrent systems, the ECM may store the vehicle ID and information about the ignition key, so be sure to thoroughly inspect it before replacement.
Conclusion
Understanding Code P2238 in a 2004 Toyota Camry is essential for owners and drivers. This diagnostic trouble code is related to the O2 Sensors Positive Current Control Circuit Low for Bank 1 Sensor 1, indicating a potential issue with the engine’s voltage control. Common causes include a faulty oxygen sensor, damaged wiring, or a malfunctioning ECM.
For those facing this error code, timely action is crucial. Checking and fixing the wiring, replacing a malfunctioning oxygen sensor, or considering an ECM replacement if needed can help resolve the issue. Regular maintenance and professional assistance will ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your 2004 Toyota Camry. By staying informed about Code P2238 and addressing it promptly, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and enjoy a worry-free driving experience.
FAQ
Replacement oxygen sensors for Toyota Camrys typically cost between $372 and $429. The expected labor cost ranges from $66 to $84.
Yes, in most cases, you can replace an oxygen sensor yourself by following the manufacturer’s instructions. It can be a cost-effective option, and you won’t need many specialized tools. Just ensure that the OEM parts you purchase are compatible with your car. However, if the O2 sensor is damaged, it cannot be repaired and must be replaced. A professional replacement will likely take less time and ensure proper installation.
While you can technically drive with a faulty oxygen sensor, it is not recommended. Your car may not stall immediately, but a malfunctioning sensor can lead to issues with the fuel mixture, resulting in engine misfires, sluggish acceleration, rough idling, and an illuminated check engine light. Promptly replacing a faulty oxygen sensor is crucial to maintain optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Neglecting the issue may also lead to potential problems, such as encountering the P2238 error code in Toyota Camry 2003 models caused by a faulty O2 sensor.